
mgibson65 in blockchain
A blockchain is known as a distributed database that preserves a list of ordered history called blocks. It is constantly developing as ‘completed blocks’. Each block has a timestamp and provides a link to former block. Blockchains are designed such a way that the data couldn’t be changed if it is once saved in database. Each node obtains a copy of the blockchain, which is downloaded automatically when it connects to the Bitcoin network. The details about the transaction to every address and the balance of cryptocurrency relating to that account are available in the blockchain.

Blockchains are secure technology by design and works like a distributed computing system including byzantine fault tolerance. Therefore, blockchain helps accomplish decentralized consensus. In this way, the blockchain becomes capable to keep record of events like medical records, management activities, transaction process, identity management and documenting provenance.
The blockchain is considered as the key technological discovery of Bitcoin, as it keeps the record of all transactions made on the network. A new block of a blockchain keeps the record of some or all of the transaction that are recently made on the network, and once it finished the task it saved into the blockchain database permanently. Each time a new block is created after a old block gets completed and saved into blockchain database. Blockchain has a number of such blocks that are not countable. They are connected to each other in accurate linear, chronological order and each block has a hash of the former block.
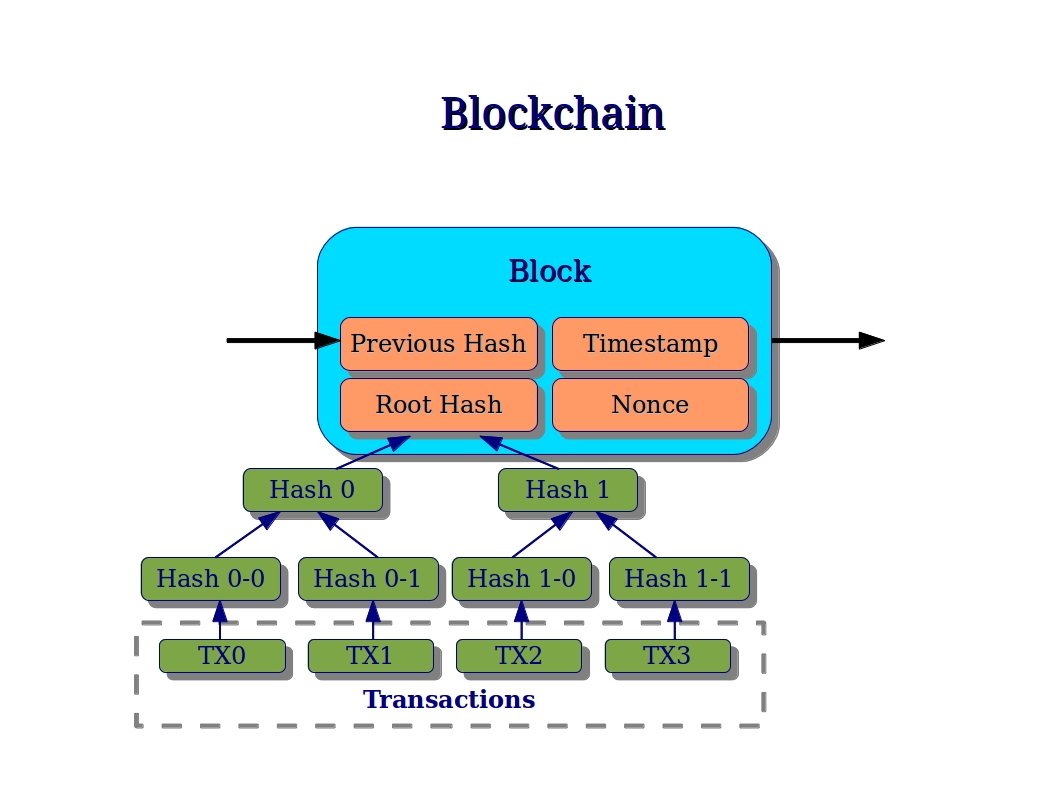
In order to use traditional banking as an analogy, the blockchain contains a complete history of banking transactions. Bitcoin transactions are recorded chronologically in blockchain database just the way that banks use to record their transactions. Blocks are just similar to individual bank statements. On the basis of the Bitcoin protocol, the blockchain database is distributed by all nodes which take part in a system. The complete copy of the blockchain contains history of every Bitcoin transaction which is ever made on the network. In this way, we can get the details of value of a transaction which is ever made to a particular address in the past. The ever-growing size of blockchain is supposed to be a big problem in future just because of its storage and synchronization. Averagely, at the interval of every 10 minutes, a new block is created and added to the blockchain through mining.
