Understanding Smart Contracts: The Backbone of Blockchain Technology
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, smart contracts stand out as a revolutionary innovation. They have the potential to transform various industries by automating and securing digital transactions. This article will delve into what smart contracts are, why they are significant in the blockchain space, and what the future holds for this groundbreaking technology.
What are Smart Contracts?
The concept of smart contracts was introduced by Nick Szabo in 1994. A smart contract is essentially a self-executing contract where the terms of the agreement are written directly into lines of code. These contracts run on blockchain networks, like Ethereum, and are designed to automatically enforce and execute the terms when predefined conditions are met.
Imagine a traditional contract: it requires intermediaries like lawyers or notaries to oversee and enforce its terms. Smart contracts eliminate the need for these intermediaries by embedding the contract's rules into the code, ensuring that the contract is executed precisely as intended.
How Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts operate on blockchain platforms, which provide a decentralized and tamper-proof environment for their execution. Here’s a basic example of a smart contract written in Solidity, a popular programming language for Ethereum:
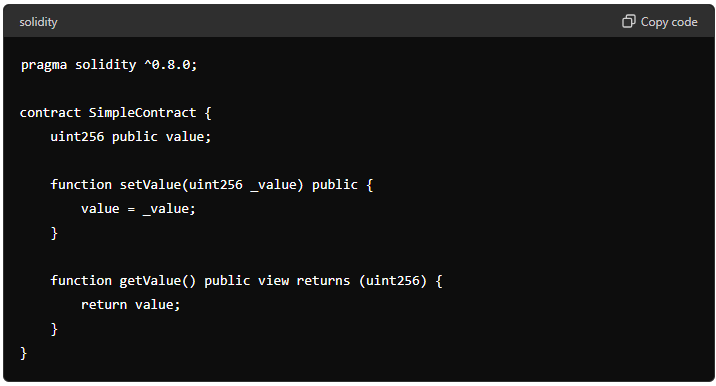
In this simple contract, users can set and get a value. The contract ensures that once a value is set, it can be retrieved by anyone, demonstrating transparency and automation.
Importance in the Blockchain Space
Smart contracts are a cornerstone of decentralized applications (dApps). They offer several key benefits:
- Decentralization: Smart contracts enable the creation of dApps that operate without a central authority, increasing resilience and reducing censorship.
- Automation and Efficiency: By eliminating intermediaries, smart contracts streamline processes, reduce costs, and increase transaction speed.
- Transparency and Trust: The terms and execution of smart contracts are visible to all participants, enhancing trust.
- Security: Operating on blockchain networks, smart contracts inherit the security features of the blockchain, making them resistant to tampering and fraud.
Real-World Applications
Smart contracts are being utilized across various industries, revolutionizing traditional processes:
- Financial Services: In decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts enable automated lending, borrowing, and trading, providing financial services without traditional banks.
- Supply Chain Management: They improve transparency and traceability by recording every transaction on the blockchain, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Voting Systems: Smart contracts can secure voting processes, ensuring transparency and preventing tampering.
- Real Estate: They streamline property transactions, reducing paperwork and ensuring that all terms are met before the transfer of ownership.
- Healthcare: Smart contracts facilitate secure patient data management and automate insurance claims, improving efficiency and privacy.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Efficiency: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, speeding up processes and reducing errors.
- Cost Reduction: Eliminating intermediaries cuts down on transaction costs.
- Trust and Transparency: The immutability and transparency of blockchain enhance trust among participants.
Challenges:
- Scalability: Current blockchain networks face scalability issues, limiting the number of transactions per second.
- Security Vulnerabilities: While secure, smart contracts are not immune to bugs and hacks.
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations: The legal status of smart contracts is still evolving, with varying regulations across different jurisdictions.
The Future of Smart Contracts
The future of smart contracts looks promising, with several trends and developments on the horizon:
- Innovations and Trends: Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) could lead to more sophisticated and autonomous smart contracts.
- Regulatory Developments: As governments and regulatory bodies better understand blockchain technology, clearer frameworks will emerge, facilitating broader adoption.
- Mainstream Adoption: While still in the early stages, smart contracts have the potential to become a standard in various industries, from finance to supply chain management.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are more than just a technological innovation; they represent a fundamental shift in how agreements are executed and enforced in the digital age. By automating and securing transactions, they offer unprecedented efficiency, transparency, and trust.
As the technology matures and overcomes current challenges, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and widespread adoption. Smart contracts are poised to play a critical role in shaping the digital economy of the future.
Disclaimer: This article is provided for informational purposes only. It is not offered or intended to be used as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.





